Money markets like Aave, Compound or Maker are the heart of the DeFi ecosystem. For the final user, these protocols have the same function than a classic bank : borrowing or putting sleepy money at work by lendind it.
Nevertheless, the analogy stops immediately at this functional comparison. Indeed, the underlying logic of money markets has nothing to do with the functioning of a bank. Money markets benefit from all the advantages of DeFi and, in particular, the transparency and accessibility of all operations.
When a user borrows on Aave, the protocol does not need to know his age or identity: validate all conditions is enough ! It means that you just have to put enough collateral.
In the same way, a user who deposits stablecoins on Aave to generate a return by lending them to others does not trust anyone: he can check at any time which amounts are borrowed by each address to ensure the solvency of the entire system.
This may seem basic to a DeFian, but it is a real paradigm shift. In traditional finance, we have no choice but to trust a third party (auditor, rating agency, etc.) to obtain this kind of information - with the reliability that we know.
Discovering money markets
We have already talked a lot about money markets on this blog, especially in the article that offers a qualitative methodology to evaluate their risks : Assessing risk in decentralized finance: a handbook for money markets
Or the one about the different services of abstraction and distribution of the inherent risks in money markets: Risk? Yes please, but exactly how I like it
However, money markets are constantly evolving, both through their updates and through the contribution of third-party services built on top. In addition, new and more challenging money markets are being launched to cover needs that are still unsatisfied.
So this is precisely our purpose today: understanding the essential innovations underway in money markets in order to better envision their future development. Rather than making an exhaustive list, I propose to look at a selection of projects that I think are relevant to understanding the industry evolution.
Innovations built on existing money markets
Money markets may seem really complex at first glance. The curious are most often frightened by the risks of liquidating the collateral when its value is no longer sufficient to secure the borrowed amount.
Easy loan positions management with DeFiSaver
Many DeFi users have not yet fully understood the issues at stake here. Many still think that liquidation can be total and sudden. In addition to information and education, tools for managing one’s positions help users to feel more confident.
Fortunately, tools that facilitate and automate the management of borrowing positions on money markets have emerged very quickly, such as DeFi Saver. I already talked about it last year in this article 🎚 ETH exposure or DeFi yields: why choose?
DeFiSaver works as a proxy between the user and money markets. It allows new features such as the well-loved “Save”: when the position falls below a user-defined collateralization limit, DeFiSaver automatically rebalances the position with a flash loan.
In concrete terms, this function sells a part of the user’s collateral to pay off some debt and return to a collateralization ratio decided earlier. Such a tool allows the most aggressive or worried borrowers to sleep much more peacefully.
Reclaiming liquidation with B.Protocol
Although DeFiSaver is very useful, it remains a tool that does not fundamentally change the way the underlying services work. Other projects go further, like BProtocol which I discovered recently.
The idea is very simple: instead of borrowing directly from Maker, the user goes through the BProtocol contract. Funds available to the protocol allows it to liquidate the user’s position (if necessary) before other liquidators do so.
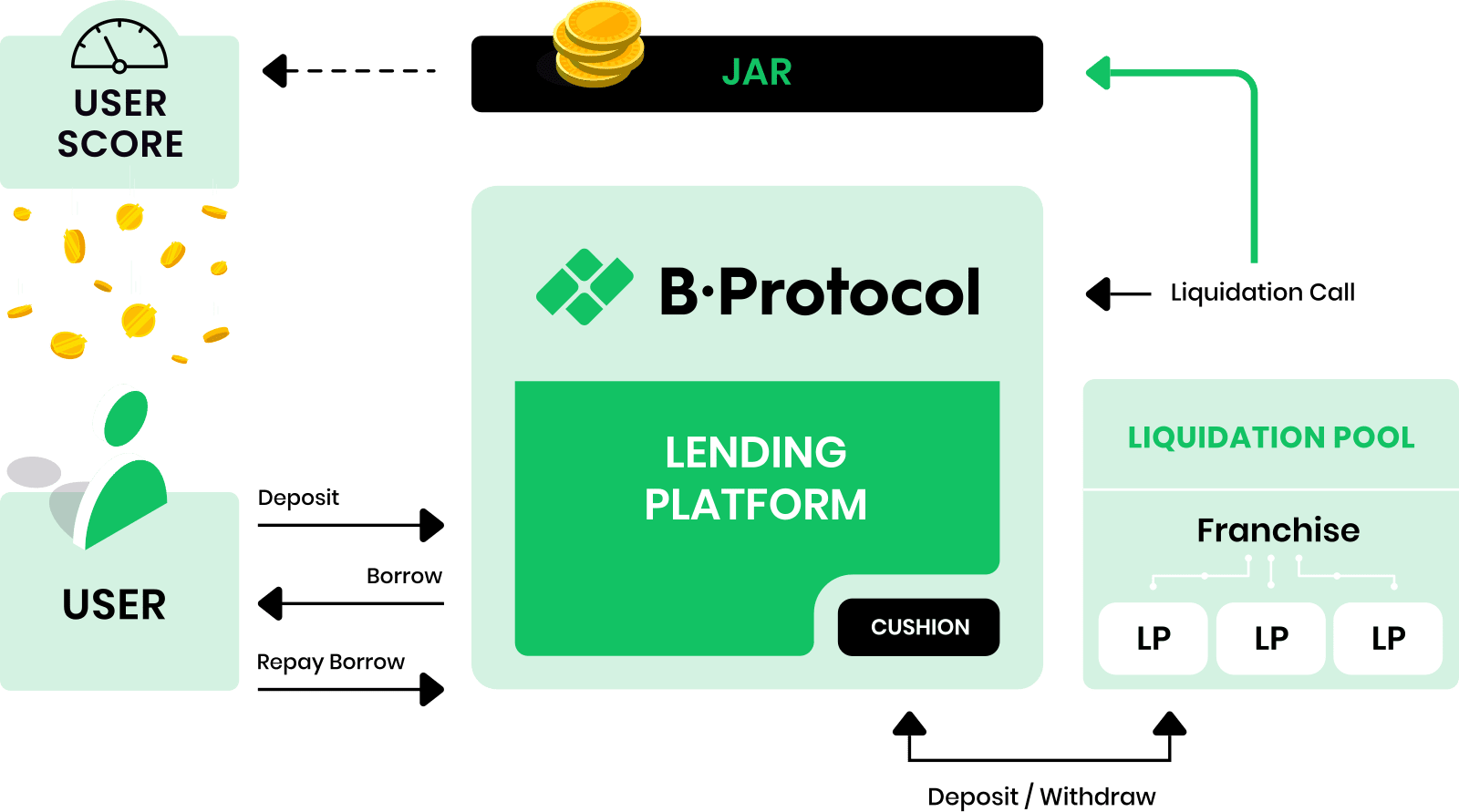 ◎ High-level explainer of Bprotocol
◎ High-level explainer of Bprotocol
What is usually a gas war between different liquidators becomes a more predictable operation. It also allows redistributing part of the liquidation premium to the user himself rather than to the miners.
Note
On money markets, users deposit collateral to borrow. If the value of the collateral is too low compared to the borrowed amount, a liquidation is necessary.
Usually this liquidation is at the expense of another type of user who gets paid (premium liquidation).
The idea, simple at a high level, is nonetheless very reassuring for users while allowing for “professionalization” of liquidations which become more predictable. There are now about $100M of assets managed by the protocol which already covers Maker and Compound (Aave is coming soon).
Innovations of the MakerDAO model
MakerDAO is probably the best-known money market, but it is also a special one. Indeed, MakerDAO serves a dual function: the service allows borrowing just like Aave or Compound, however no one lends you anything when you borrow on Maker - borrowers directly mint a currency (DAI) that corresponds to their debt.
Thus, while allowing borrowing, MakerDAO also produces a stable asset, the DAI, which is indexed on dollar. Although DAI has its limitations, it is less centralized and requires less trust than stablecoin models like USDC. This is why Maker’s model has been taken up many times to serve new purposes.
Mimo Capital: down with the dollar, up with the euro!
Until now, the dollar has been the reference fiat currency for DeFi. Almost all stablecoin projects aim to produce an asset that tracks the value of the dollar. In addition, it is also the dollar value of volatile assets that is considered by borrowing systems to determine the collateralization ratio, both on Maker and Compound or Aave.
The dollar being the most common and best known fiat currency, it made sense to start with but it is time to go beyond that to meet the needs of all types of users and make DeFi more accessible.
This is precisely what a project like Mimo Capital is looking for, as it proposes a system similar to MakerDAO but where the Euro is the base currency, instead of the dollar. This means that the stablecoin produced by the borrowers - the PAR - follows the Euro, but also that the internal prices of the system are in €, as the value of the collateral used (ETH, wBTC or USDC).
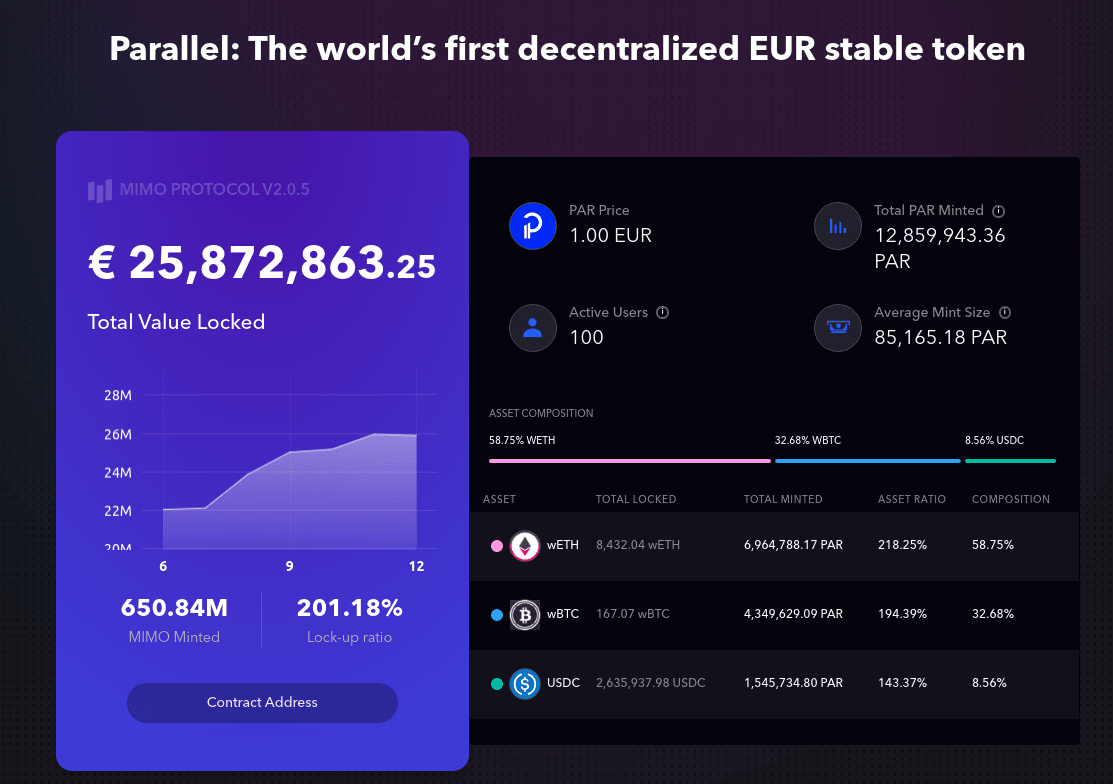 ◎ The main metrics for PAR, from the official website.
◎ The main metrics for PAR, from the official website.
Mimo is not coming up in an empty market as Euro stablecoins are beginning to emerge. In addition to Mimo’s PAR, there is the EURS stablecoin which follows a centralized model: each EURS in circulation is backed by a Euro fiat owned by the issuer. Thus, yield opportunities are starting to emerge via Euro exposures, for example the sEUR/EURS pool on Curve also accessible via vaults on StakeDAO or Harvest Finance.
The arrival of a protocol like Mimo allows European investors to consider a circuit with the Euro as the reference currency. Using their ETH or wBTC as collateral, they can borrow PAR (stablecoin €) and make it productive via, for now, two liquidity pools on Balancer, but eventually, probably more.
Mimo is still a fairly new system with approximately €25 million of collateral deposited as collateral for approximately 12.5 million PARs issued (€). The governance token associated with the service - MIMO - is currently distributed to any active vault holder as well as to liquidity providers on the PAR/ETH and PAR/USDC pairs.
Beyond fiat currencies with Reflexer
Switching from dollar to euro is good, going completely without a fiat currency reference is even better This is exactly what Reflexer, another service inspired by the Maker model, offers.
There is no reference price here. The price of the RAI (borrower-generated asset) is governed directly by the market (average price on the RAI/ETH pair). The system also has its “internal” price, the Redemption Price - the rate used when users directly mint RAI (by depositing ETH as collateral).
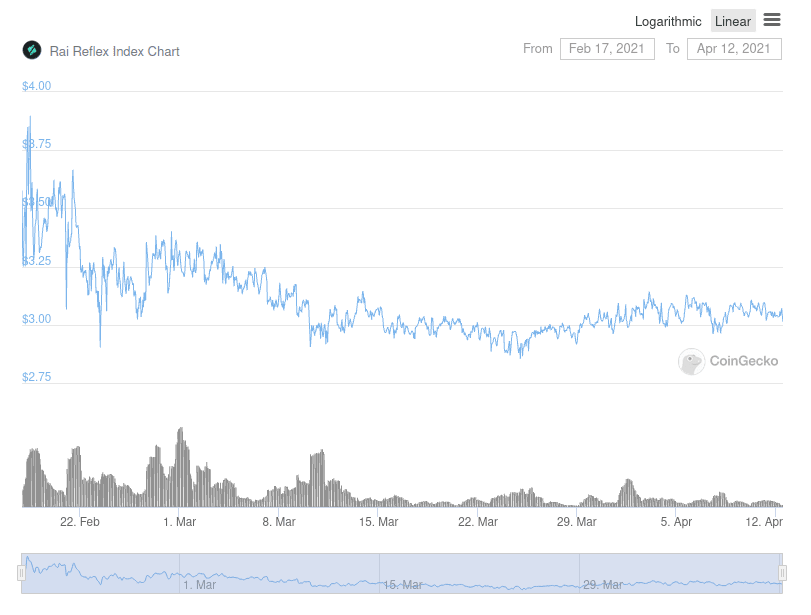 ◎ RAI price evolution since its launch
◎ RAI price evolution since its launch
Various parameters in the Reflexer system adjust to converge the two prices over time, or at least keep them within a narrow range. While this approach is much more difficult for the user to learn, it is completely uncorrelated with the dollar (or any other fiat currency), which is valuable in itself.
To better understand Reflexer, I recommend you to read my previous article on stable assets:
Exploring stable assets on Ethereum: approaches & endgame?
New generation of money markets
So far, we have considered innovations built on the existing core money markets or directly inspired by their models. There is also a whole new wave of money markets exploring different approaches.
I therefore propose to consider two final projects that bring real fundamental changes.
Alchemix: productive assets as collateral?
I couldn’t start this section with another project than Alchemix! The idea of this project is as simple as powerful:
- What if, instead of taking non-productive collateral, we only took productive collateral like a stablecoin that produces a return ?
- Our collateral now has a return: what if the return on the collateral was used to pay off the loan?
- And there you have it: A loan that pays for itself over time!
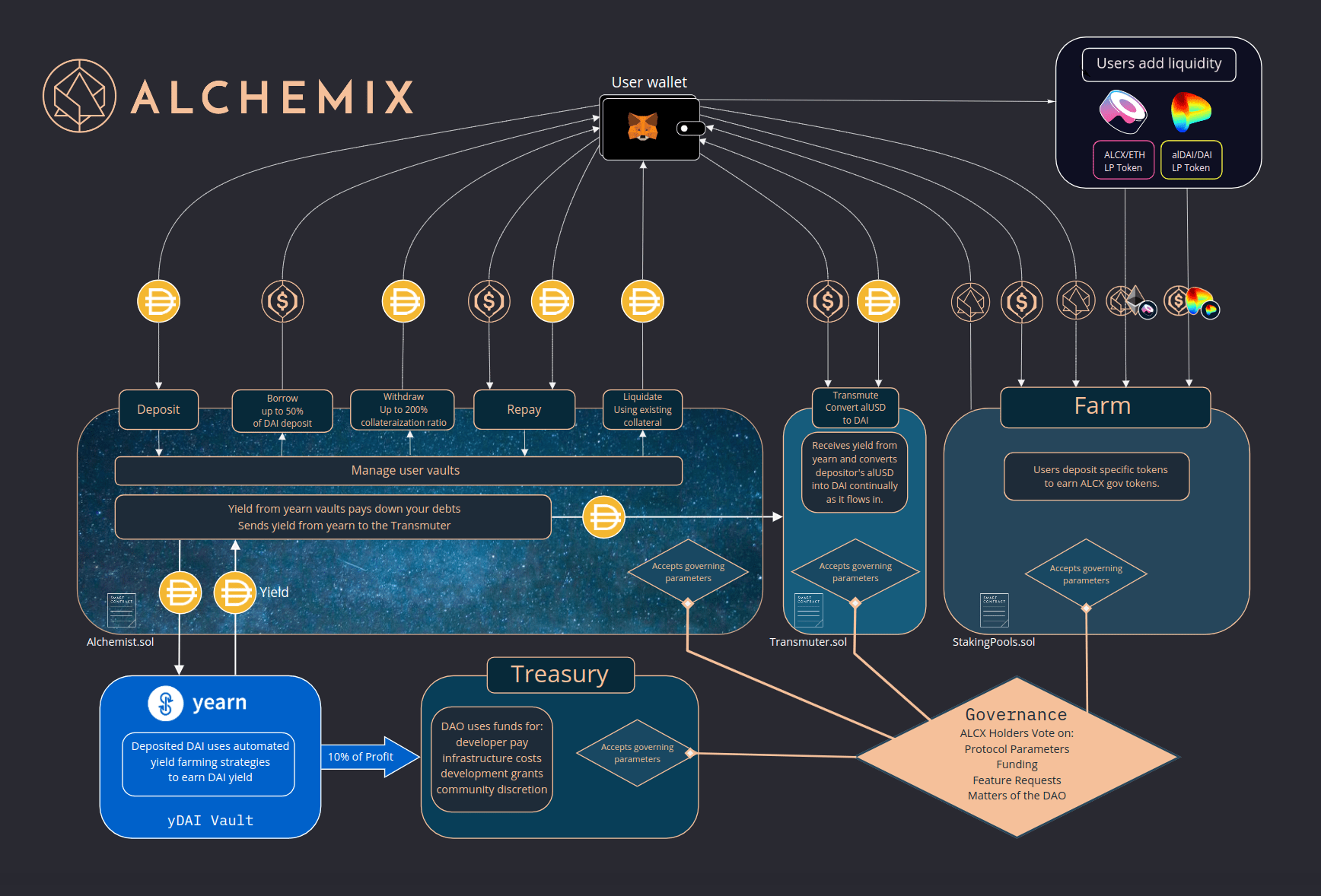 ◎ Alchemix architecture
◎ Alchemix architecture
Alchemix launched by accepting yDAI (DAI deposited on Yearn Finance) as collateral. Depositors can borrow up to 50% of the value of their yDAI in AlUSD, another stablecoin dollar. Their collateral is not at risk, and the loan pays for itself through the interest generated by the yDAI: it takes about 3 years at the current return rate.
Alchemix quickly became a very popular service, especially for proceeding large purchases without spending crypto, it’s just a matter of patience. Let’s take an example.
This is Bob, a DeFi farmer who has worked hard: he now wants to enjoy the fruits of his labor. He wants to raise $50,000 to buy a car. Rather than taking $50,000 directly from his assets, Bob can achieve the same result without spending anything thanks to Alchemix :
- Bob deposits 100,000 DAI on Alchemix, which are then deployed on Yearn
- This allows him to borrow up to 50,000 AlUSD, which he can use to buy his car.
- Bob just has to wait while the yDAI returns pay back his loan. In ~3 years, once the debt is paid off, he can get his original 100,000 DAI back.
Such flow allows to spend immediately without any other cost than the fact of locking about 2 times the amount mobilized within Alchemix. The future of programmable money is live!
It is so powerful and innovative that many still find it hard to believe. The feedback from Alchemix users still attracts many skeptics:
Liquity: efficiency at all costs
Liquity is another money market that innovates on several levels. The fundamental concept to understand here is that liquidations are automated and therefore much more predictable and quick.
This allows Liquity to offer lower collateralization ratios than other systems, or to put it another way: Liquity users can raise more dollars per ETH deposited than on a system like Maker:
Info
The maximum loan-to-value ratio (maximum LTV) determines the borrowing power of a collateral. A maximum loan-to-value of 50% means that up to half of the dollar value of the deposited collateral can be borrowed.
- Maker : minimal ratio = 150% ⇒ approximately 66% max LTV
- Liquidity : Collateralisation minimal ratio = 110% ⇒ approximately 90% max LTV
Liquity also innovates on the fees side since the loans are interest free unlike other systems. On Maker/ETH for example, the stability fee is 5.5%. If you borrow 10,000 DAI today, you will have to pay back 10,550 DAI in 1 year (if the fees do not change).
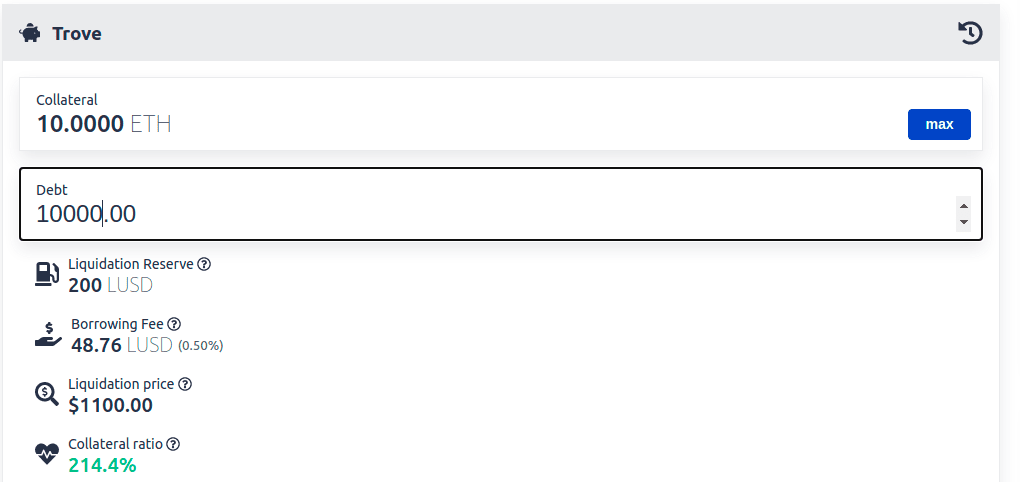 ◎ A loan with no interest and no fees other than 0.5% of borrowing fee paid immediately
◎ A loan with no interest and no fees other than 0.5% of borrowing fee paid immediately
On the other hand, there is no stability fee on Liquity. Instead, users pay a one-time, immediate fee when borrowing. This fee depends on the “base rate” which is governed by the protocol directly. It is currently 0.5%.
On Liquity, those who deposit ETH to mint LUSD can then deploy them into the Stability Pool (LUSD) or the LUSD/ETH pair for remuneration in LQTY - the service’s native token.[1] The LQTY can then be staked to get a share of the LUSD paid to the protocol when a loan is contracted as well as the redemption fee (ETH ↔ LUSD).
Note
Liquity is a so-called “governance mimized” platform - LQTY is therefore not a governance token.
Finally, Liquity also innovates in terms of decentralization since the interface used to access the service is not managed by the team behind the protocol. Different frontends operated by third parties are offered while the team focuses on the protocol itself. This ensures that many mirrors exist so that the service is always easily accessible.
The next step to understand money markets
I hope you have found this introduction to the latest innovations in the money markets informative. I’m delighted to see the offering growing and becoming denser to cover ever more varied needs. Money markets are essential elements of DeFi, and with the growth of the space, they will become more and more preponderant.
Finally, let me remind you that in addition to functionality, risk management is the essential element that differentiates each money market. Before you start spending large sums of money on them, I invite you to familiarize yourself with the associated risks. It’s a good thing, I wrote what remains to this day the most exhaustive and comprehensible synthesis to understand the risks incurred in the money markets, I invite you to read it:
Assessing risk in decentralized finance: a handbook for money markets
🙏 Huge thanks to HHK, Charles, Thomas, Erwan, PhilH & FrenchTony for proofreading the French version of this article and translating it integrally into English.
You’ll find more info regarding the LQTY token distribution in the official documentation.